Introduction
By no means complete, November’s mini guide that follows provides notes for exploring various interesting deep sky objects (DSOs) and lists other items of interest useful to the amateur astronomer.
Entries can be interpreted based on designation, description and magnitude as follows.
Designation – Description – Magnitude:
★ Telescopes 10-inch aperture minimum.
★★ Telescopes 6-inch to 9-inch aperture.
★★★ Binoculars (50mm+ aperture) and telescopes
3-inch to 5-inch aperture.
A collimated instrument, favourable atmospheric conditions, dark skies and dark-adapted eyes are assumed.
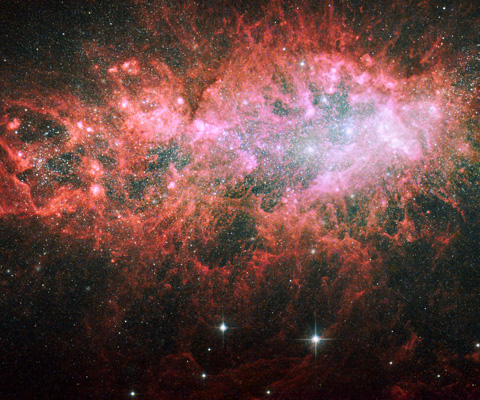

The NGC 1569 galaxy. Image taken by NASA/ESA
Hubble Space Telescope.
About NGC 1569
This image taken by NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope showcases the brilliant core of one of the most active galaxies in our local neighbourhood. The entire core is 5000 light-years wide.
The galaxy, called NGC 1569, sparkles with the light from millions of newly formed young stars. NGC 1569 is pumping out stars at a rate that is 100 times faster than the rate observed in our Milky Way Galaxy. This frenzied pace has been almost continuous for the past 100 million years.
The core's centrepiece is a grouping of three giant star clusters, each containing more than a million stars. (Two of the clusters are so close they appear as one grouping.) The clusters reside in a large, central cavity. The gas in the cavity has been blown out by the multitude of massive, young stars that already exploded as supernovae. These explosions also triggered a violent flow of gas and particles that is sculpting giant gaseous structures. The sculpted structure at lower right is about 3700 light-years long.
Huge bubbles of gas, such as the two at left, appear like floating islands. The largest bubble is about 378 light-years wide and the smallest 119 light-years wide. They are being illuminated by the radiation from the bright, young stars within them. Some of those stars are peaking through their gaseous cocoons.
The biggest and brightest objects surrounding the core are stars scattered throughout our Milky Way Galaxy. In contrast, the thousands of tiny white dots in the image are stars in the halo of NGC 1569. The galaxy is 11 million light-years from Earth.
A new analysis of NGC 1569 shows that it is one and a half times farther from Earth than astronomers previously thought. The extra distance places the galaxy in the middle of a group of about 10 galaxies centred on the spiral galaxy IC 342. Gravitational interactions among the group's galaxies may be compressing gas in NGC 1569 and igniting the star-birthing frenzy.
Hubble's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 and Advanced Camera for Surveys made the observations of NGC 1569 in September 1999, November 2006, and January 2007.
Image credit: Credit for Advanced Camera Data: NASA, ESA, A. Aloisi (STScI/ESA), J. Mack and A. Grocholski (STScI), M. Sirianni (STScI/ESA), R. van der Marel (STScI), L. Angeretti, D. Romano, and M. Tosi (INAF-OAB), and F. Annibali, L. Greggio, and E. Held (INAF-OAP).
Credit for Wide Field Planetary Camera 2 Data: NASA, ESA, P. Shopbell (California Institute of Technology), R. Dufour (Rice University), D. Walter (South Carolina State University, Orangeburg), and A. Wilson (University of Maryland, College Park).
Observation guide
| November deep sky objects |
| Taurus constellation |
|
Hyades
|
An open star cluster consisting of hundreds of stars.
|
|
★★★
|
|
NGC1514
|
A planetary nebula with a 9th magnitude central star. Instruments of 10 inches aperture or greater will reveal some nebulosity round the fast-rotating binary star in its centre.
|
10.0
|
★★
|
|
M45
|
The Pleiades star cluster is surrounded by gas and dust only visible in large instruments. Otherwise, the cluster is best observed with binoculars due its relatively large apparent size.
|
1.39
|
★★★
|
| Cassiopeia constellation |
|
M103
|
Open cluster with around 170 stars.
|
7.0
|
★★★
|
| Perseus constellation |
|
NGC869
|
An open cluster with around 500 stars. The NGC884 and NGC869 can be viewed at the same time as they are only 30’ apart.
|
5.30
|
★★★
|
|
NGC884
|
Open cluster with around 500 stars. Binoculars and wide field instruments should offer impressive views of the two clusters. The cluster is home to five 8th magnitude red supergiant stars.
|
6.10
|
★★★
|
|
M76
|
The Little Dumb Nebula is an apparently small but bright planetary nebula that can be viewed in average sized instruments. Detail increases with aperture revealing its interesting structure in large instruments.
|
12.0
|
★★
|
|
M34
|
Open star cluster. Only the brightest stars are visible in instruments of average size. At least 19 of its members are white dwarfs.
|
6.0
|
★★★
|
|
NGC1245
|
Open cluster with around 200 stars.
|
6.90
|
★★
|
|
NGC1275
|
A faint galaxy that appears as an oval of light. CCD cameras will reveal its structure.
|
12.7
|
★★
|
|
NGC1023
|
A barred lenticular galaxy and a member of the NGC1023 group of galaxies.
|
10.5
|
★★
|
| Camelopardalis constellation |
|
NGC1560
|
A spiral galaxy relatively close to Earth.
|
12.1
|
★★
|
|
NGC1569
|
An irregular dwarf galaxy close enough to Earth for the Hubble Space Telescope to resolve stars within it.
|
11.8
|
★★
|
|
M1
|
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant with a neutron star in the middle. The star exploded around 2,000 years ago and was visible for 23 days significantly outshining Venus. Visible in a 4-inch instrument under good conditions it will reveal some detail in 12-inch instruments and above.
|
9.0
|
★★★
|
|
NGC1501
|
A planetary nebula with its central star only visible in larger instruments.
|
13.3
|
★★
|
|
NGC1502
|
An open cluster of 20 stars.
|
5.30
|
★
|
| Eridanus constellation |
|
NGC1535
|
A planetary nebula will reveal structure in instruments above 8 inches in aperture. The central star may be possible to observe in very large instruments.
|
9.30
|
★★
|
|
|
Designation, Description, Magnitude
|
★ Telescopes 10-inch aperture minimum.
★★ Telescopes 6-inch to 9-inch aperture.
★★★ Binoculars (50mm+ aperture) and telescopes 3-inch to 5-inch aperture.
|
The night sky
Under excellent conditions over 2,000 stars can be seen with the unaided eye but only a few hundred of these are prominent enough to be useful in navigating the night sky, these are normally included in amateur sky maps and digital planetarium programs like the SkySafari, Stellarium, The Sky, Starry Night, Winstars 2 etc. Some stars will show colour that is useful in identifying them. For example, Antares, Betelgeuse and Aldebaran are orange/red where Vega, Rigel and Spica appear as blue/white.
Stars that form easily recognisable patterns have been given names and are referred to as constellations. Of these, the brightest stars act as beacons and can be used to effectively navigate the night sky during the different months of the year. To that extent stars can be particularly useful in locating other interesting objects nearby normally viewable through binoculars or larger instruments.
Planets and their satellites, comets and meteors move independent of the night sky background and at comparatively high speeds. They are therefore very difficult or impossible to reference to any star. However, planets like Jupiter, Saturn, Venus and Mars as well as the Moon are easy to spot with the unaided eye and in the case of the larger planets and especially the Moon, even medium size binoculars will reveal a limited degree of detail.
About NGC 1275
This stunning image of NGC 1275 was taken using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys in July and August 2006. It provides amazing detail and resolution of the fragile filamentary structures, which show up as a reddish lacy structure surrounding the central bright galaxy NGC 1275. These filaments are cool despite being surrounded by gas that is around 55 million degrees Celsius hot. They are suspended in a magnetic field which maintains their structure and demonstrates how energy from the central black hole is transferred to the surrounding gas.
By observing the filamentary structure, astronomers were, for the first time, able to estimate the magnetic field's strength. Using this information they demonstrated how the extragalactic magnetic fields have maintained the structure of the filaments against collapse caused by either gravitational forces or the violence of the surrounding cluster during their 100-million-year lifetime.
This is the first time astronomers have been able to differentiate the individual threads making up such filaments to this degree. Astonishingly, they distinguished threads a mere 200 light-years across. By contrast, the filaments seen here can be a gaping 200,000 light-years long. The entire image is approximately 260,000 light-years across.
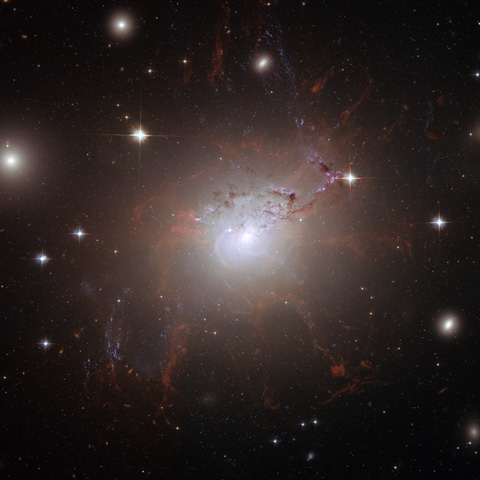

The NGC 1275. Credit: NASA, ESA and Andy Fabian (University of Cambridge, UK).
Also seen in the image are impressive lanes of dust from a separate spiral galaxy. It lies partly in front of the giant elliptical central cluster galaxy and has been completed disrupted by the tidal gravitational forces within the galaxy cluster. Several striking filaments of blue newborn stars are seen crossing the image.
Image credit: NASA, ESA and Andy Fabian (University of Cambridge, UK).
Sky conditions
The prevailing sky conditions will have a significant effect on what you can see through any instrument and binoculars. As such if you live near a city the light pollution can make it difficult to locate and observe most DSOs. The Moon and a hazy sky will also have a negative effect.
For best results observe from a dark site and under clear transparent skies without the moon being present. Once your eyes have been accustomed to the dark conditions (this takes around 20-30 minutes) you should be able to enjoy the night sky at its best.
Filters
Filters will help to an extent and lager instruments will benefit more from them. Light pollution filters would help and photo-visual UHC (nebula filters) would be worth considering.
Printed aids
A huge number of printed aids exist in terms of deep sky maps and books. An excellent printed guide for people new in astronomy is The Year-Round Messier Marathon Field Guide published by Willmann Bell Inc.
In this large format hard-back book, the author, Harvard Pennington shows how to:
- Learn 17 bright finder stars and 17 prominent finder constellations so you will know where to look for all 110 Messier objects.
- Align a sighting device such as an 8x50 finder scope or the Telrad® so that you can point your instrument rapidly and with assurance toward all of the Messier objects.
- Calibrate your instrument so that you know exactly how much sky you see through your finder and through the eyepiece of your instrument.
- Find all of the Messier objects using the maps, drawings and descriptions in this book. You will know exactly where to point your instrument, and what the object should look like when you find it.
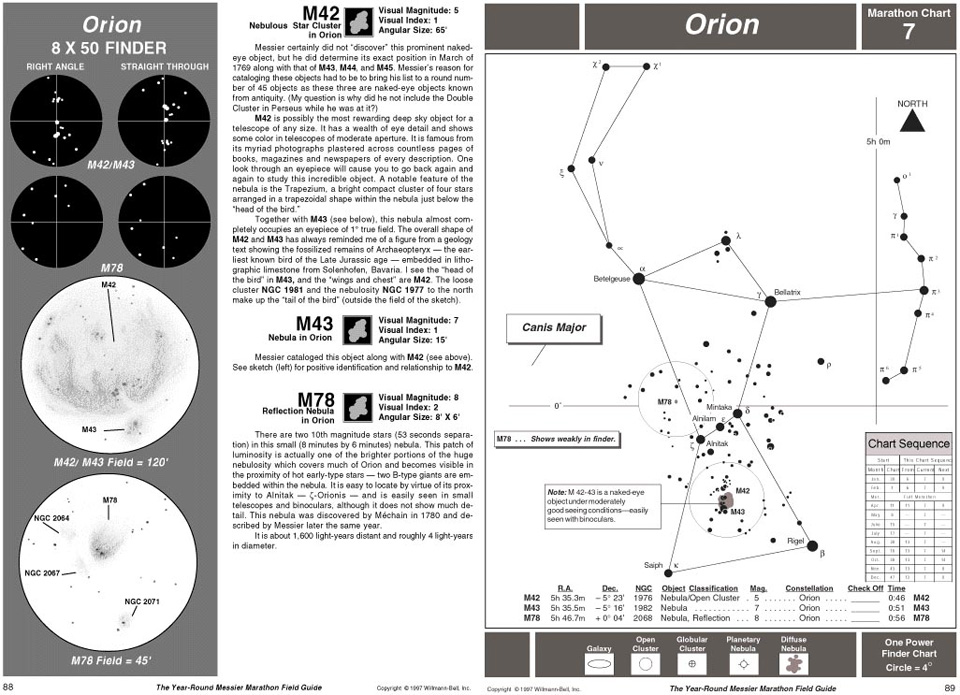
Extract from The Year-Round Messier Marathon Field Guide
published by Willmann Bell Inc.
Related topics:
night sky, deep sky object guide, November



